Yesterday I was reminded during one of my sessions that revisiting the best ideas and the best advice is important.
In today’s blog post I want to share the best and most effective methodology of learning a piece of text off by heart. The method is one used by many actors to learn their lines, and is certainly one that can be used if you or your child takes on a large part on stage. I teach the same method to my tutees as a means of learning the translation of their Latin set texts off by heart, the purpose of which is to make the literature element of the examination super-easy.
Let us take for example the first few lines of Sagae Thessalae, the most commonly-studied prose set text for the current OCR specification for GCSE Latin. Below is the first section of the Latin text, with a suggested translation underneath. It is the translation that your child will need to learn off by heart (not the Latin – that really would be a nightmare!)
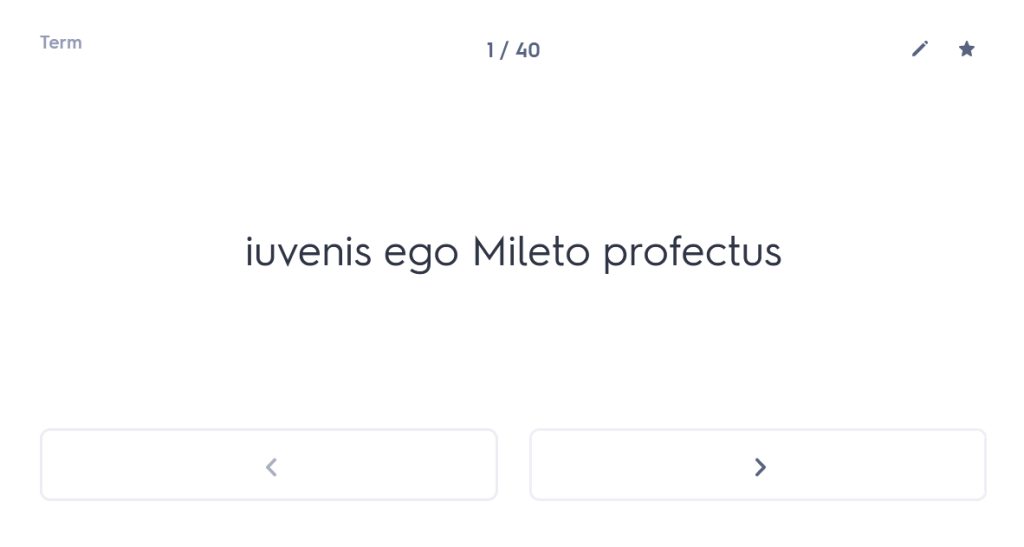
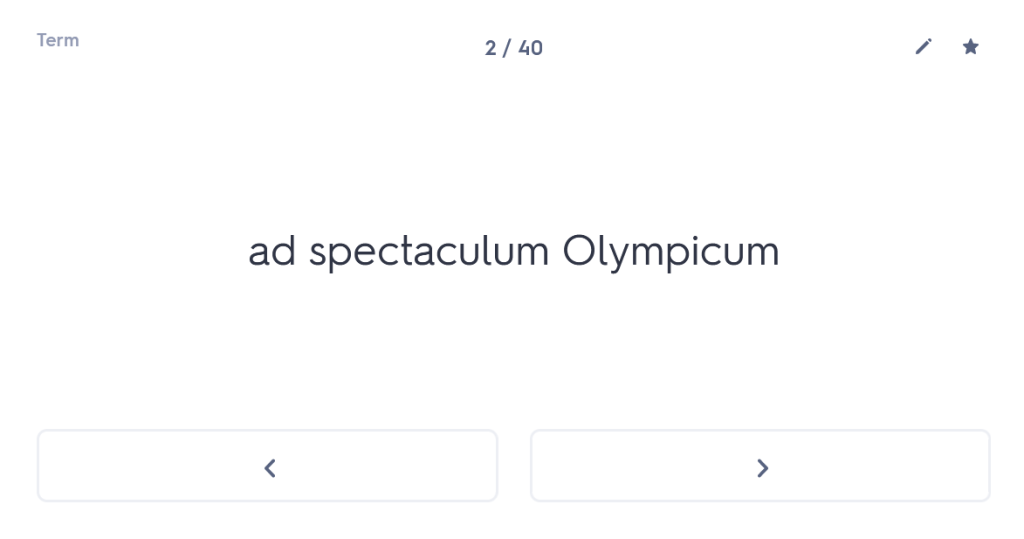
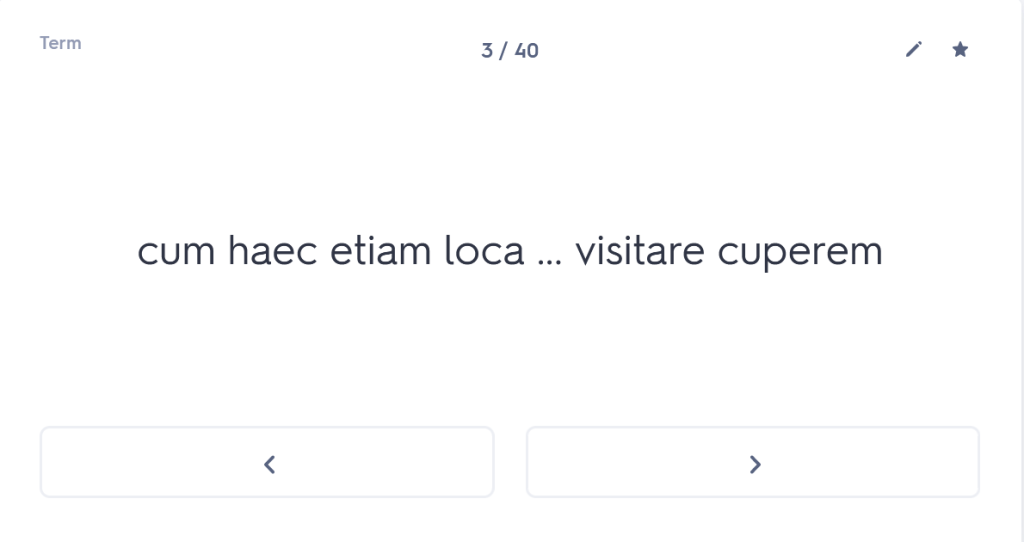
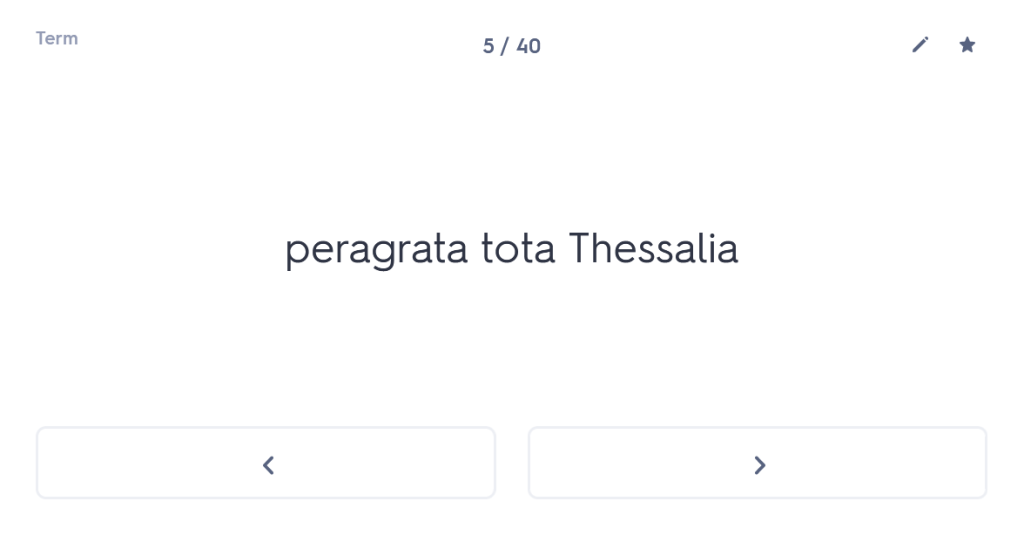
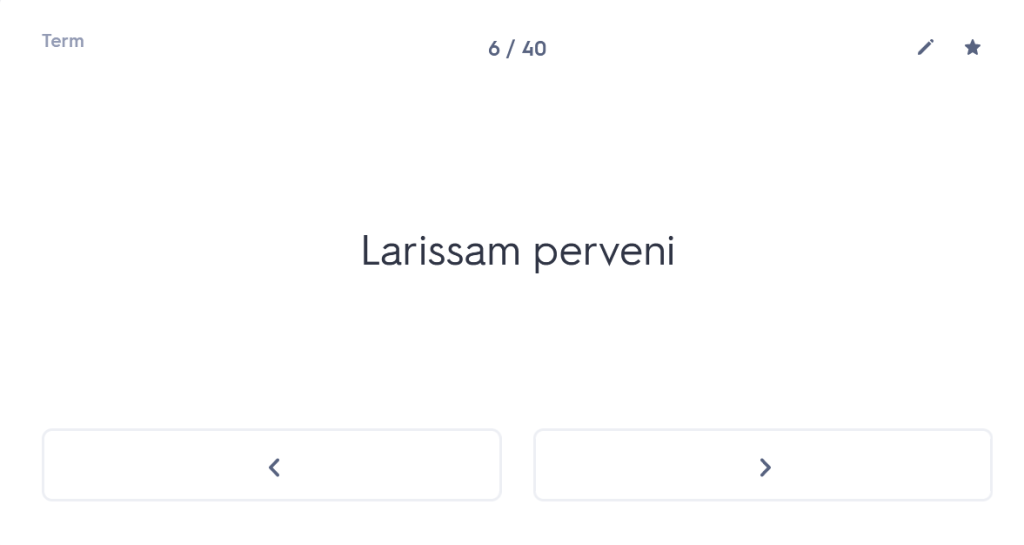
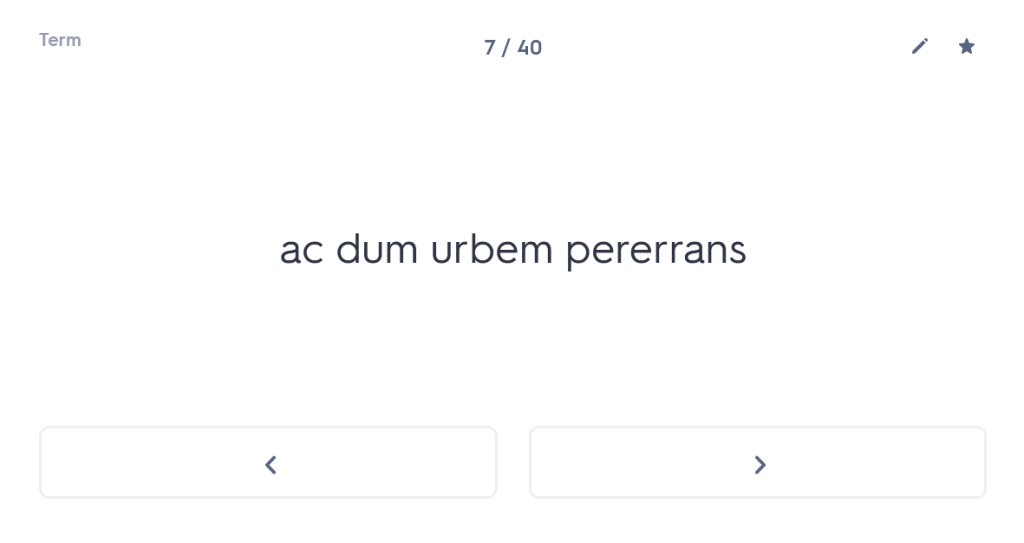
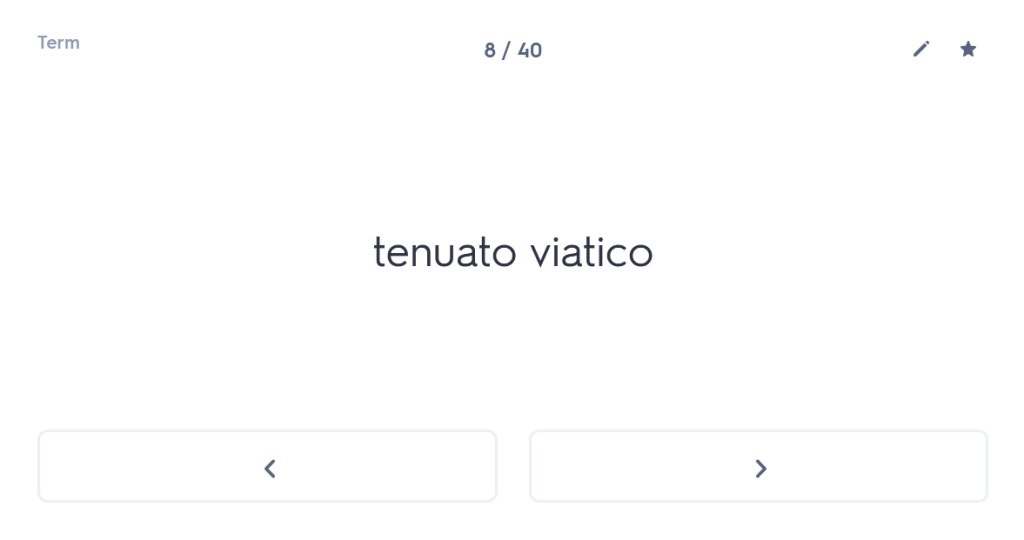
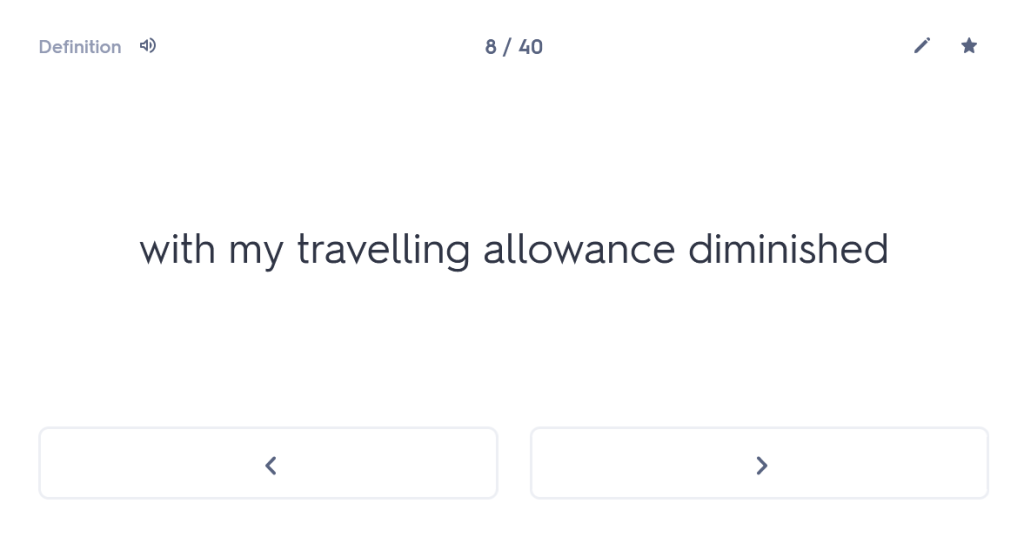
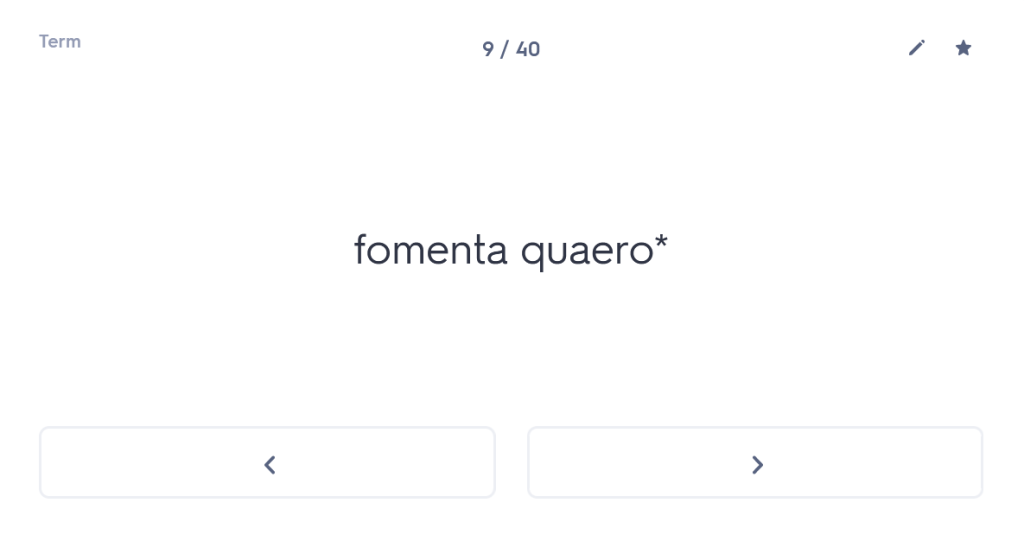
iuvenis ego Mileto profectus ad spectaculum Olympicum, cumhaec etiam loca provinciae clarae visitare cuperem,peragrata tota Thessalia Larissam perveni. ac dum urbem pererrans tenuato viatico paupertati meae fomenta quaero.
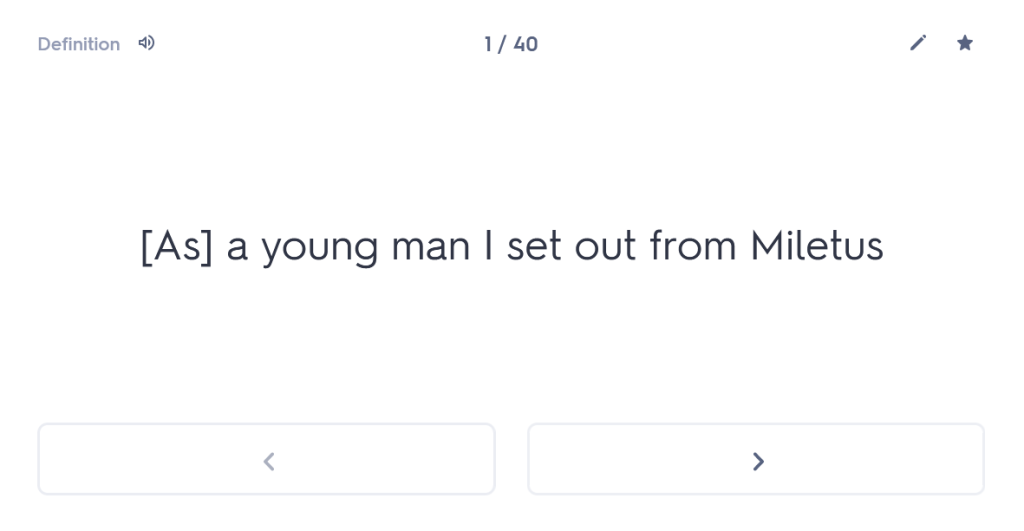
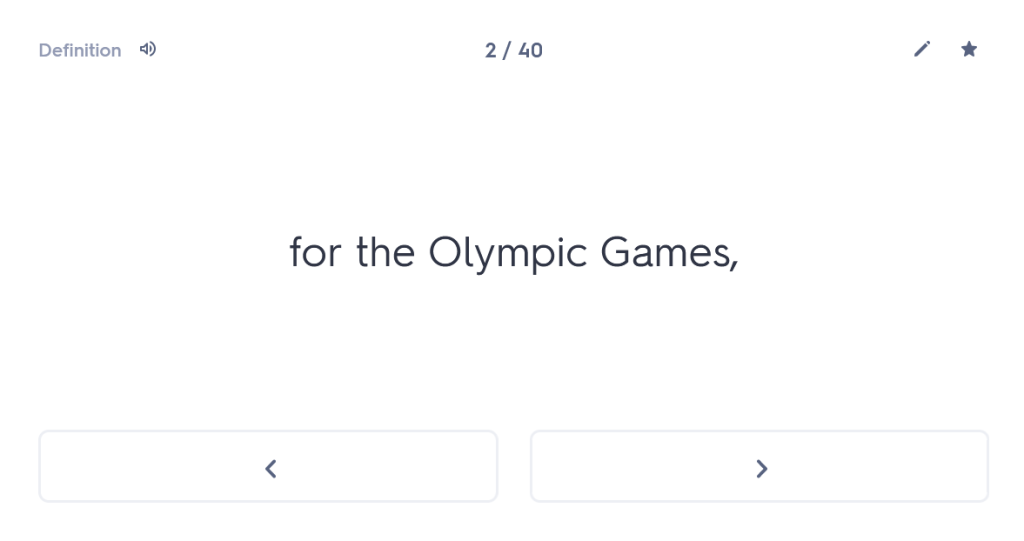
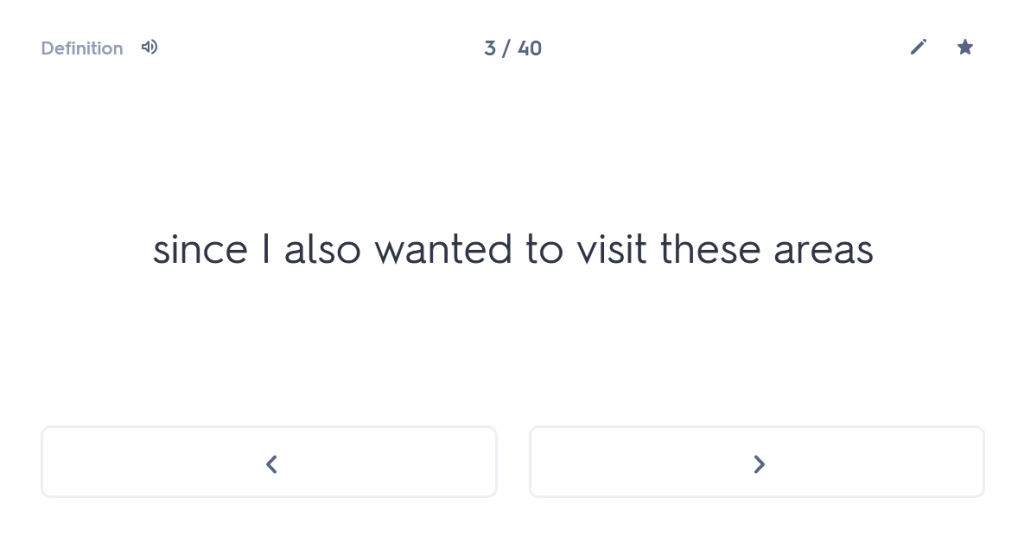
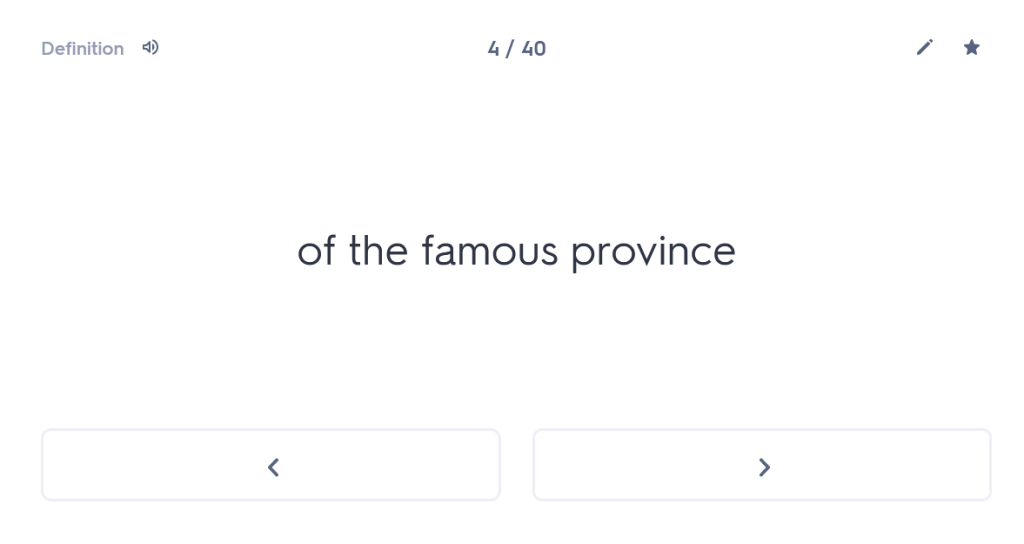
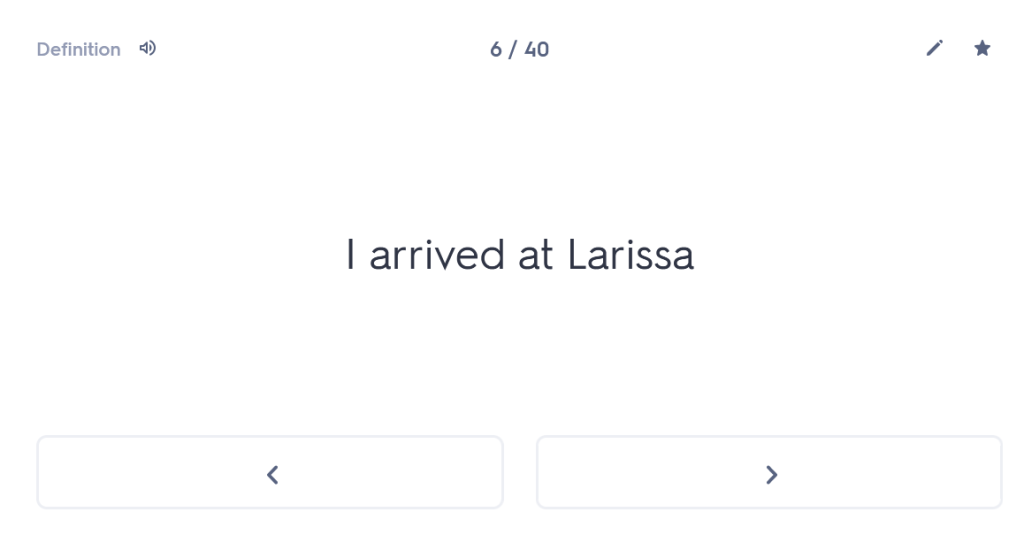
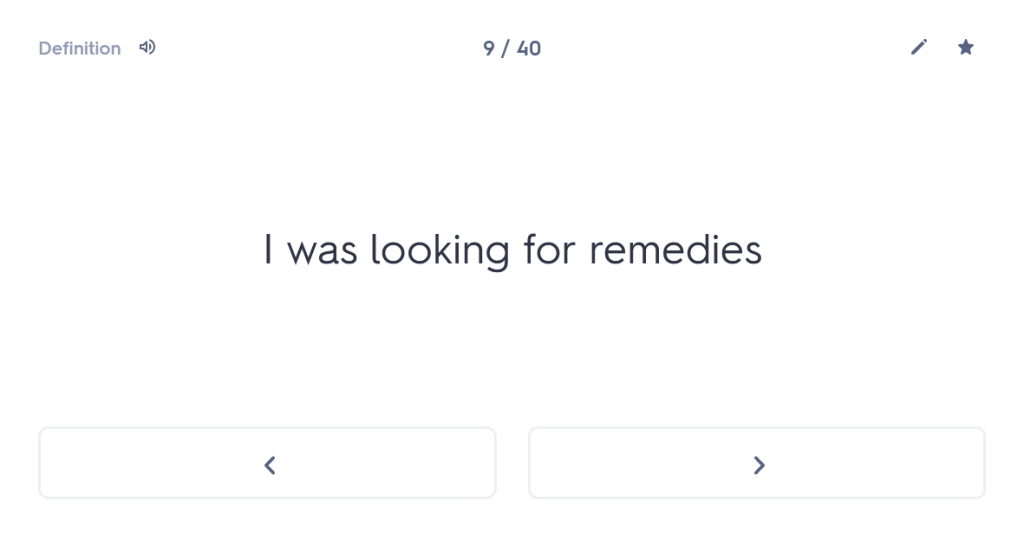
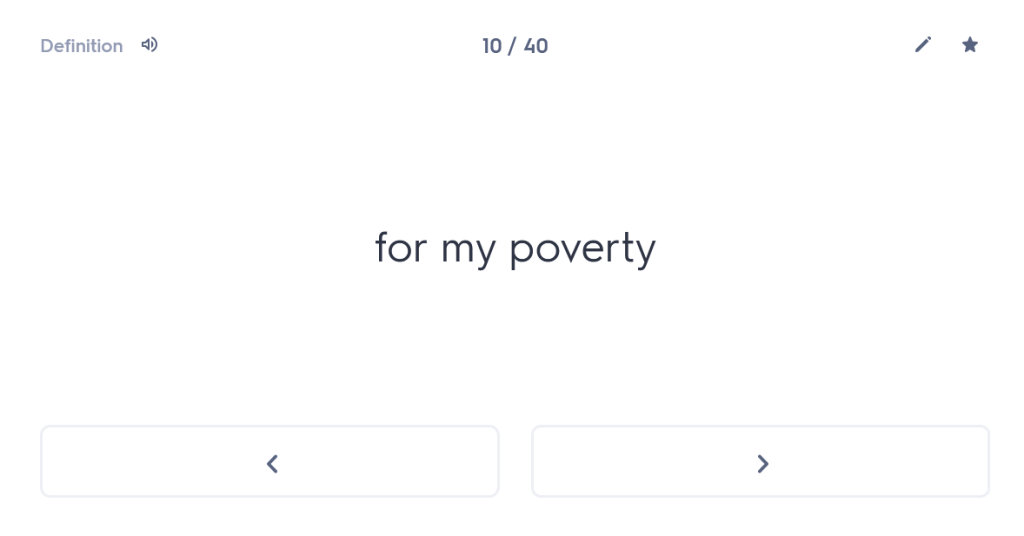
“As a young man I set out from Miletus for the Olympic Games, since I also wanted to visit these areas of the famous province. Having travelled through the whole of Thessaly, I arrived at Larissa. And while wandering through the city, with my travelling allowance diminished, I was looking for remedies for my poverty.”
To go about learning a section like this, the best thing to do is to break it up into sections and learn it using the first-letter technique. The passage breaks up quite nicely into five short chunks as follows:
As a young man I set out from Miletus for the Olympic Games,
since I also wanted to visit these areas of the famous province.
Having travelled through the whole of Thessaly, I arrived at Larissa.
And while wandering through the city, with my travelling allowance diminished,
I was looking for remedies for my poverty.
Below is a representation of the first-letter technique for these lines. A student writes down the first letter of each word, spaced out in short chunks. Notice that I have used the punctuation – making use of capital letters, commas and full-stops acts as a further trigger for the memory:

While most people will struggle to learn these five sections of prose off by heart, the use of chunking combined with the first-letter technique enables most people to do so within a couple of minutes. Once a student has written out the first chunk in first letters, they should find that they are immediately able to recite the first chunk merely by looking at the letters. They should then repeat the process with the remaining chunks, then try to recite the whole thing, using the letters as a prompt. Within a couple of minutes, their ability to recall the entire passage will be notable. Students can then go on to repeat the process with the remaining text – not too much at once though!
Once a student has mastered the translation of a reasonable amount of text, that’s the time to turn to the Quizlet flashcards. It’s important not to wait too long to do this, as the rote-learning of the English translation will not be much use to a candidate without at least some grasp of how it relates to the Latin. A child who has learnt the translation off by heart should be able to use the flashcards to prompt themselves on each section as follows:




You will notice that I have divided the flashcards into smaller chunks – this is to assist the student in recognising which Latin words and phrases map onto which sections of the translation. There will be some hesitation as a student learns to map their rote-learned translation onto the Latin as represented on the flashcards – but that’s fine. Remember, the rote-learning is merely a prop to assist them in coping with the set text in an examination. It’s very important to move onto the flashcards swiftly, in order to begin the process of making the rote-learned translation do its job of supporting the student in recognising the Latin text.
A student should repeat the flashcards in chronological order until they are fully confident with the translation for each. Once confidence has been gained, it’s then time to hit the shuffle button and see if they can recognise and translate small chunks in isolation – that’s when they can really prove to themselves that they are recognising individual Latin words and phrases and can render them into English.
The whole process might seem arduous when a student first begins, but I have yet to find a student that is not converted to the the system once they realise how effective it is and how much power it gives them over the text. Knowing the text thoroughly is 80% of the battle – and I mean that sincerely. A student should be able to score a pretty good grade in the literature element of the examination simply on the basis of knowing the text really well; many of the questions are comprehension and ask for nothing more than for the student to explain what the text means. Once a student has gained mastery with a section of the text and can perform well on basic comprehension questions, then time can be spent on fine-tuning their response to the text and training them in how to answer the more complex questions, something which I have addressed in other posts.






