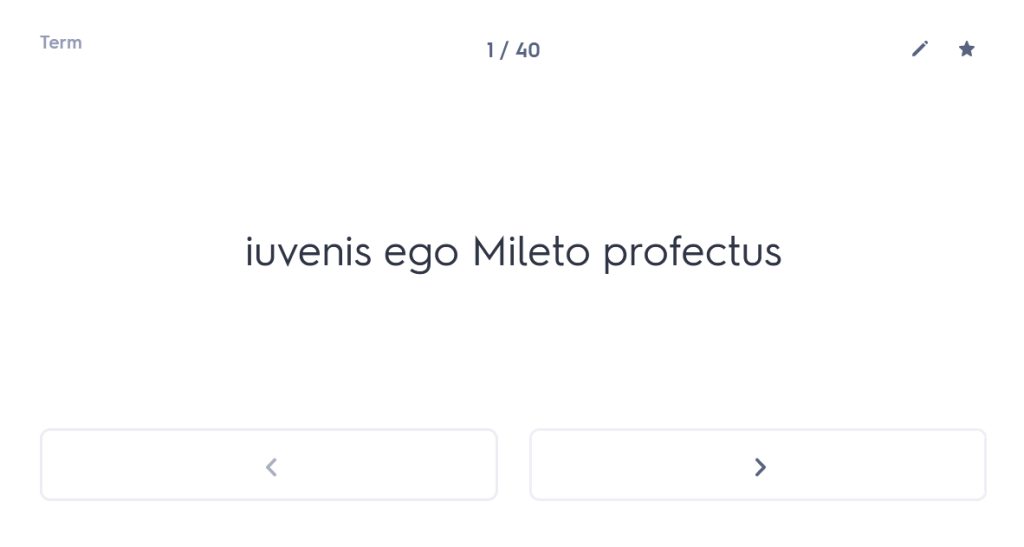
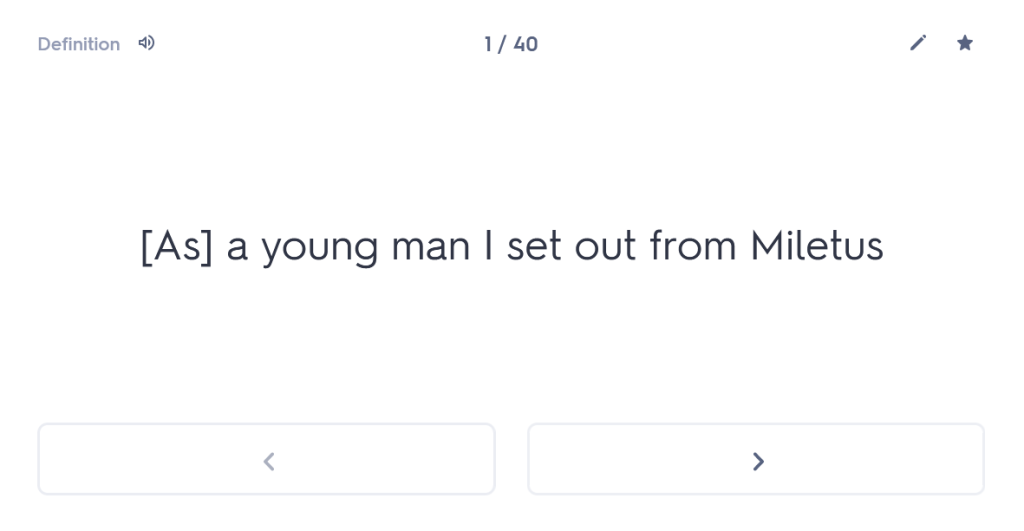
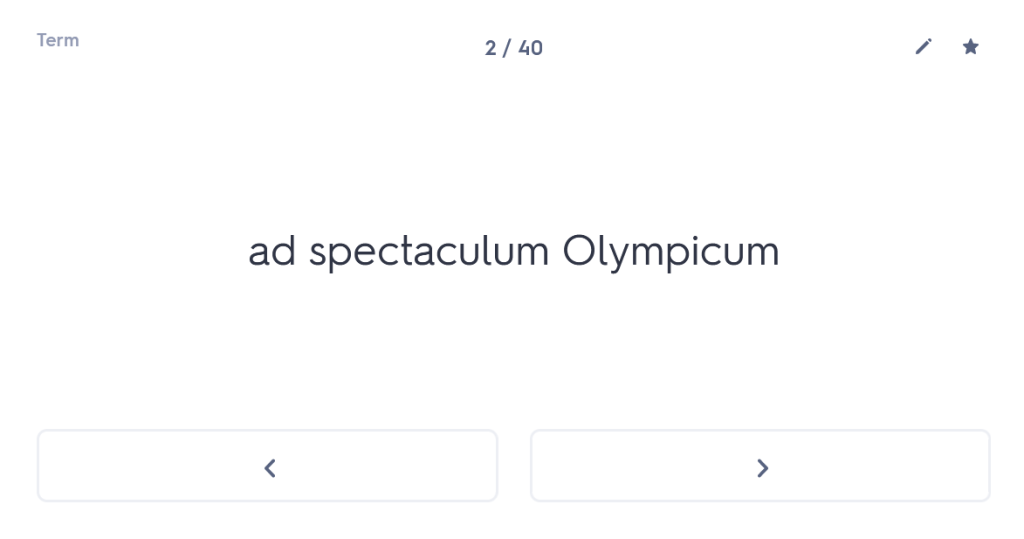
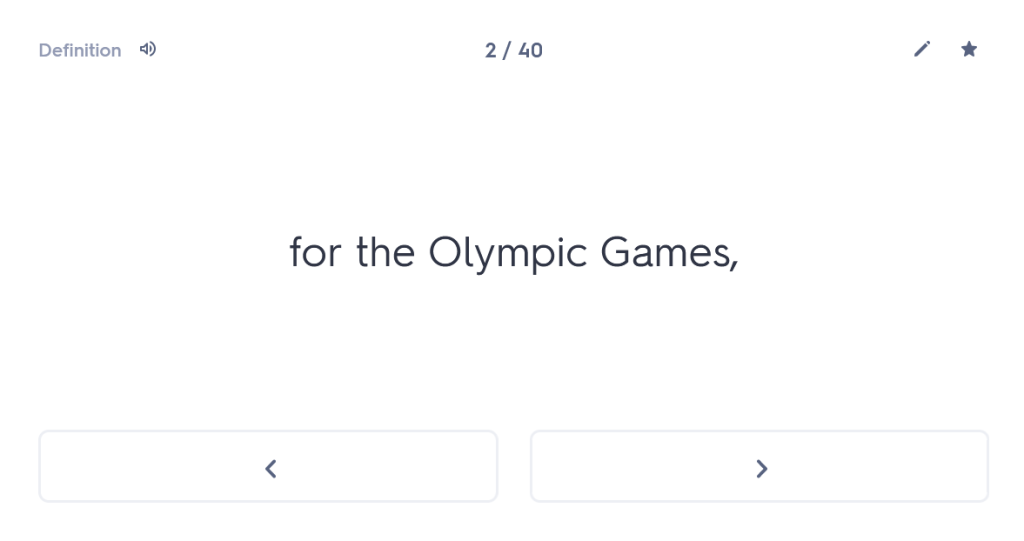
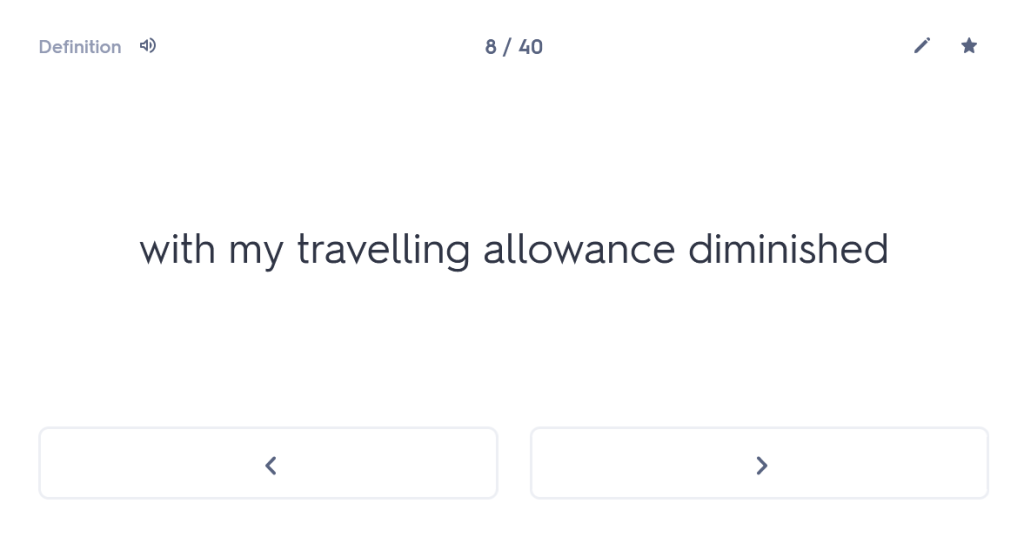
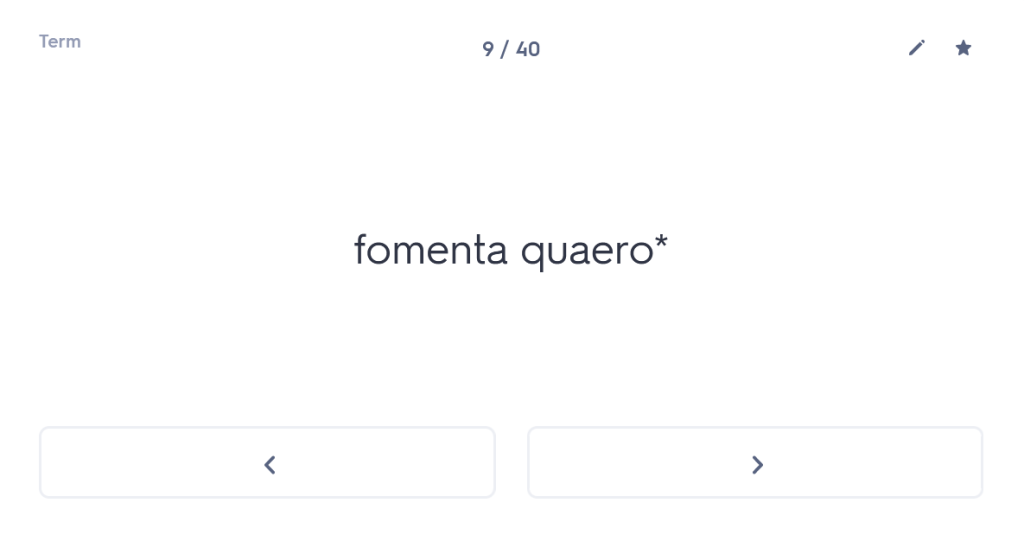
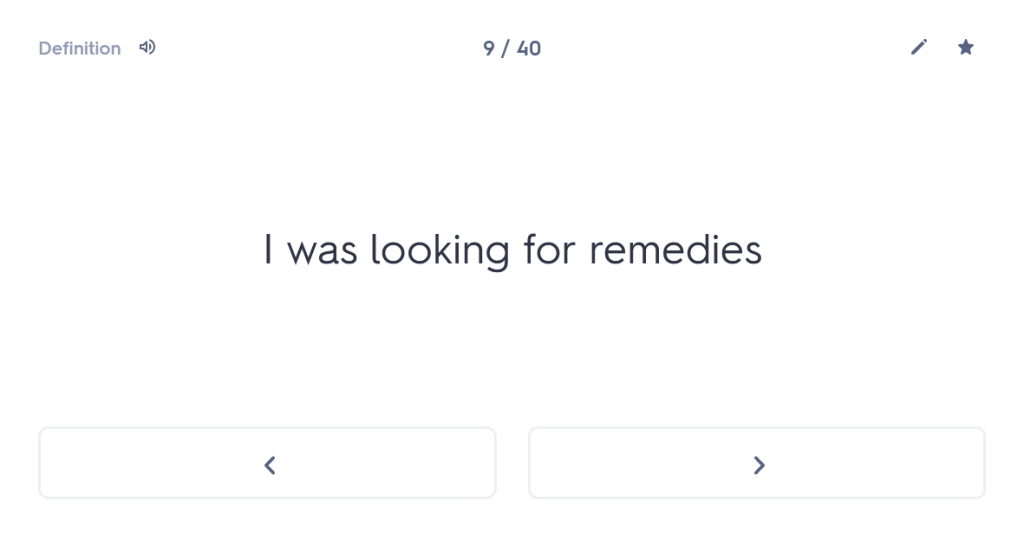
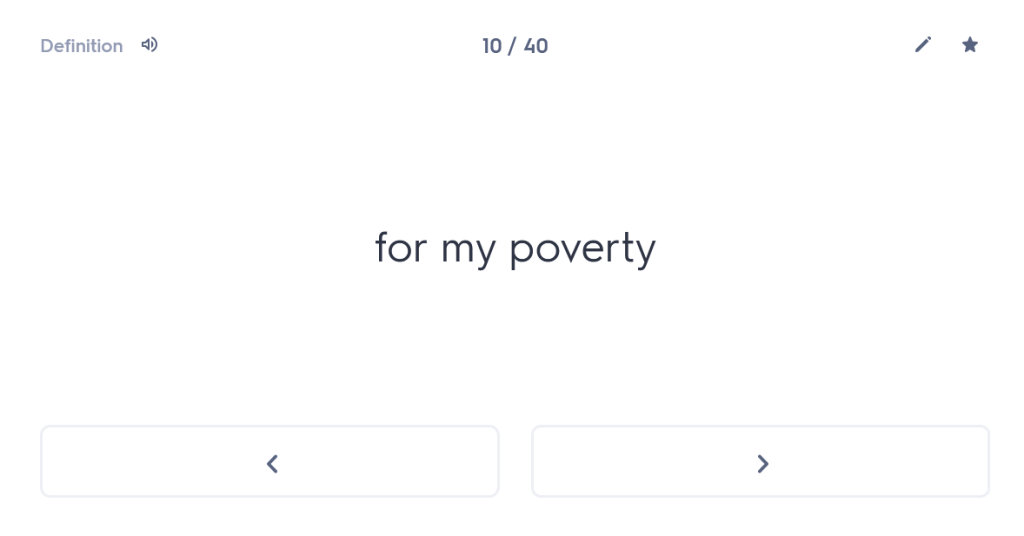
Many people undestimate the importance of forgetting time. I’m not talking about forgetting painful experiences here (although the ability to wipe those from one’s memory might also be considered rather useful); I’m talking about giving your brain time to “forget” what it has learned, purely so that you can force it to remember again. Think that sounds weird? Well, let me persuade you.
Memory, as cognitive scientist Daniel T. Willingham so famously defined it, is the residue of thought. Students will struggle to remember things which they have not thought deeply about and the best teachers use a combination of methods to get students to think actively about what they need to remember. There has been much welcome discussion in recent years about retrieval practice in the classroom, and alongside that the importance of spaced learning. Believe you me, this was not the focus during my teacher-training 21 years ago, indeed there was little to no interest shown by the lecturers in how memory works, little focus on the inescapable fact that a child’s success or failure in the education system is defined by their ability to use their memory effectively – both their working memory and their longterm memory.
In the simplest possible terms, a person’s working memory is what they use to process information and acts like a kind of holding pad. Memory expert Tracy Alloway describes the working memory as like a post-it note: capable of holding only a tiny amount of information temporarily, and not suitable as a system for longterm storage. For effective learning to take place in the classroom, it is crucial that a student’s working memory is not overloaded and a large part of that responsibility rests with the classroom teacher. However, students themselves (and those supporting them) can help too. The more a student can do to transfer knowledge into their longterm memory (which, unlike the working memory, is limitless) the better their capacity to learn will be. In my subject, this means that the student should endeavour to learn as much vocabulary as they can, as well as the important noun and verb endings; this will mean that they are not over-burdened in the classroom, enabling them to access more learning.
So there’s the rub. How exactly does one transfer knowledge reliably into one’s longterm memory? Well, the more I work one-to-one with students and advise their parents and guardians, the more I have come to understand that most of them really underestimate the importance of forgetting time.
Some students have been taught about spaced learning in school, as part of a drive towards empowering them with a knowledge of metacognition (which is thinking about thinking – a knowledge of how we learn – exactly what we’re talking about now). This is fantastic. In schools that are switched on to this, students are taught to repeat their self-testing processes regularly, leaving a gradually-increasing length of time between each revisit. Some schools teach a fixed process, helping students by advising them on exactly how long those varied gaps should be, but the truth is that it doesn’t necessarily matter. In principle, students should be regularly testing themselves on things they learnt that day, that week, that fortnight, that month, that year; the best and most effective kind of retrieval draws on a range of learning distances.
Students can actually exploit their brain’s capacity for forgetting and retrieval during very short spaces of time, and I make this happen within my 30-minute tutoring sessions. As one simple example, I might help a student commit the endings of the 1st declension to memory in the first few minutes of a session. I might then test them on a series of nouns which follow the first declension. I will then return to the endings of the 1st declension and test them on those again at the end of the session. That’s a typical 30-minute lesson arc and allows for “forgetting time”. However, even within that arc, I will further exploit the brain’s ability to switch from one focus to another and, as a result, to temporarily forget; during the process of testing a student on the 1st declension endings, once they reach a certain level of competence, I might suddenly ask them a couple of random questions to distract them from the table: do they know how many declenions there are? What gender are most nouns in the 1st declension? Can they think of any words that they know which follow the pattern of the 1st declension? Once their brain has been distracted for a minute or or so by this Q&A, I will then ask them to recall the endings of the 1st declension once again. The constant exploitation of forgetting time increases the impact of learning because it is forcing the brain to retrieve something which has briefly exited the working memory (i.e. the student has not spent the last minute actively thinking about it and holding it in their head).
Perhaps the most important thing that students need to know is that forgetting is crucial. Forgetting is therefore not the enemy; forgetting is part of the learning process. Once students gain confidence with this, what they begin to realise is that their brains take less and less time to recall what they have seemingly forgotten with each reboot. The process of recall in and of itself is what cements learning and is crucially important. I have written before about the dangers of the forgetting curve, as posited by psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus, when it comes to memorisation; but what the forgetting curve actually shows is that forgetting is not just inevitable, it is an integral part of the memorisation process. We cannot learn a large amount of information without allowing ourselves time to “forget” it prior to forcing ourselves to recall it again.
It is therefore important to reassure students that retrieval can and indeed should feel a little uncomfortable – you are forcing yourself to try and remember, and in these days of Google that is not something we do very much. Many a happy evening was spent back in the day when a friend might say “who wrote that song?” and one would spend several minutes (or several hours!) trying to remember collectively. Now we can just look up the answer, we’re perhaps less trusting of the fact that if we wait long enough, the answer will pop into our heads. As Daniel T. Willingham puts it, “people usually believe that forgetting happens over time; if you don’t use a memory, you lose it. This may be hard to believe, but sometimes the memory isn’t gone—it’s just hard to get to.” This is the most remarkable thing demonstrated in the whole process – you might think you’ve forgotten something, but the memory is actually there, lurking deep inside your brain. Retrieval teaches you how to access it.
So let’s hear it for forgetting. Forgetting is important. Forgetting should be exploited as part of the learning process. And let’s face it, forgetting is unavoidable. All we can do is work with it.

who made the art of seeming to forget his trademark