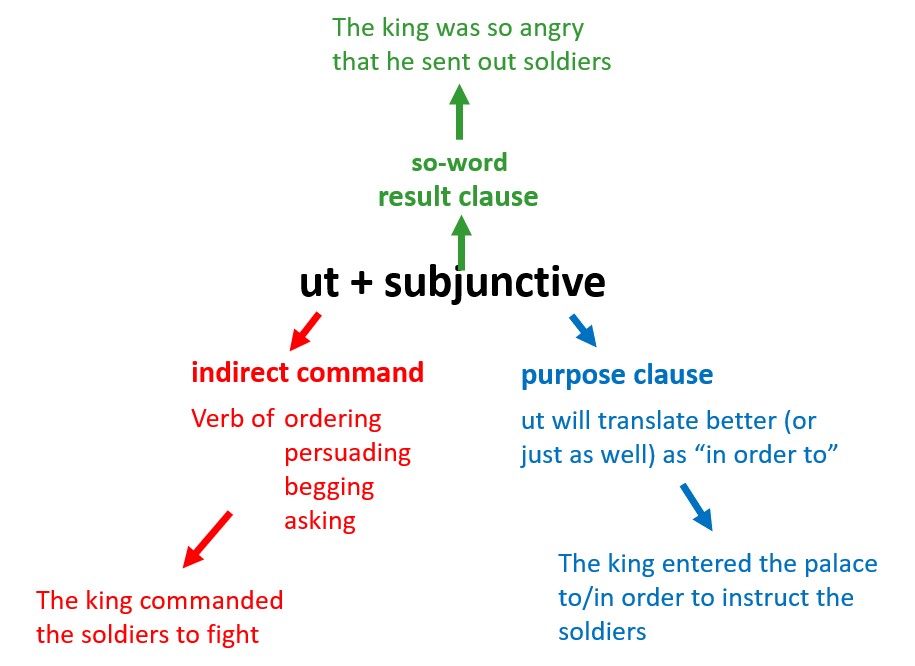
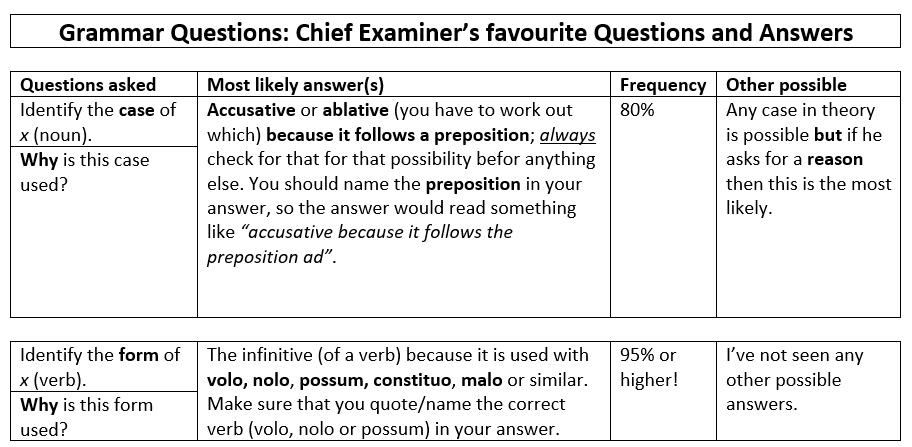
One of the many joys of tutoring is the time and space it affords you to check out whether a student understands basic concepts. This does not only mean basic academic concepts, such as the differnce between the subject and the object; it also means looking at some of the ostensibly simplest sorts of questions on the exam papers and making sure that they know how to go about them.
Teachers of Latin GCSE are under enormous pressure to get through the syllabus content in the time they have available. Latin classes – certainly in state schools – often start from a position of disadvantage, having already had a limited number of teaching hours at Key Stage 3; some GCSE classes even start ab initio. The exam board then demands that a huge amount of complex material is covered, including a ludicrous amount of real Latin literature. The reality of this means that class minutes are at a premium, and teachers will move rapidly over basic concepts and may even assume that simple questions are understood and do not require practice. Often, as a direct result of this, key marks are lost due to small misconceptions or a lack of clarity in a student’s mind when it comes to how to approach such questions.
This week I finally got around to reading the Examiners’ Report from 2023 and their comment on the derivatives question really leapt out at me. It said, “this question is designed to be accessible to candidates of all abilities, and most scored at least 2 marks.” Personally, I find this utterly delusional on the part of the examiners. How, pray tell, is a question accessible to all candidates when it relies on a breadth of literacy and general knowledge not covered in the syllabus itself? And how is a score by many of 50% on this question indicative that it was indeed accessible? The comment is simply astonishing and I’m afraid it betrays yet again how out of touch the world of Classics is with reality. I have worked with a variety of students who have been scuppered by the derivatives question and their struggle is due to one or more of the following reasons:
- Students do not know their Latin vocabulary well enough to be able to access the question. You can’t come up with a viable derivative if you don’t know what the Latin word means. This is more complex than it perhaps sounds, as the word is often presented in a form that is different from the one they have learnt e.g. dabat from the verb do), meaning that candidates who find the subject challenging will probably struggle to recognise it.
- Students are EAL (English as an Acquired Language) and lack the breadth of English necessary to succeed in this question. They may be performing outstandingly well in the subject, but they have not yet come across the word regal or sedentary.
- Students do have English as their first language but are not widely read, meaning that they struggle to come up with derivatives; they might recognise one when it’s pointed out to them, but they find it difficult to reach for one. This means that students for whom reading is modelled and encouraged at home are at a huge advantage, which is one of the main reasons why the examiners’ assertion that this question is “accessible” really grinds my gears.
- Students have simply not been taught how to approach this question, or if they have been shown how they have not practised it at length. Teachers rarely spend a significant amount of time doing so because they assume (like the examiners do) that the question is easy. Plus, as I mentioned earlier, it may be time they do not have. In my experience to date, the best schools practise deivations from the very beginning of Key Stage 3, and this is certainly the best way to embed the knowledge for GCSE.
Some students really do have no problem with the derivatives question, and when that’s the case I leave them to it. These students are always highly literate and usually well-read. Unlike them, many students need to be shown multiple examples of derivatives and time needs to be invested in guiding them through the vocabulary list looking for such derivatives – the examiners even recommend this in their notes, yet still cling to the delusion that this question is highly accessible. Believe me, any question that cannot be done without detailed, explicit, one-to-one guidance from an expert is not accessible; teachers do not have time on the curriculum to prep for this question adequately.
Another question that many teachers lack the time to focus on and tend to assume the students will cope with just fine is the 10-marker in the literature papers. Because the question is open-ended and requires no knowledge of the Latin, this question really is accessible in the sense that even students who have struggled with the material should be able to do it; I say “should” because once again there is some guidance required. Students tend to apply what they have been taught about answering other types of questions (even in other subjects) to the 10-marker and this can lead them down the wrong path; answers need to be full of quotations/references but not to the Latin, to the text in translation. There is also no requirement for detailed analysis. I have written about this in more detail here. The 10-mark question makes up 20% of each literature exam: that means it makes up 10% of a student’s entire result – way more than the difference between two grades. It’s definitely worth spending some time on!
It’s a real joy as a tutor to be able to dive into the basics and make sure that students are well-prepared for what they face when it comes to exam time. Questions that the examiners and teachers assume are easy usually are so once you know how to approach them, but it’s that assumed knowledge that I’m interested in. Once a student has been gifted with said knowledge, that’s when they can start to fly.