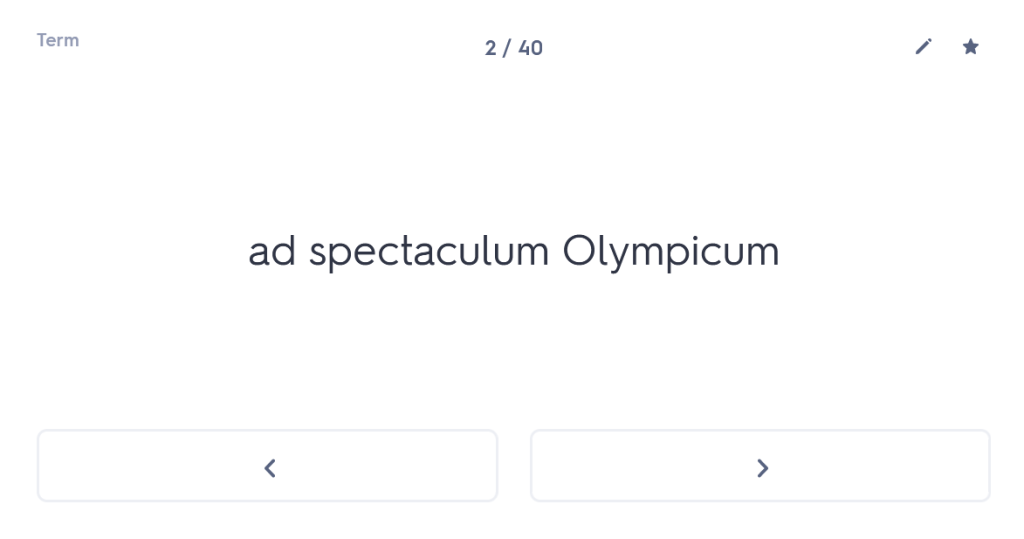
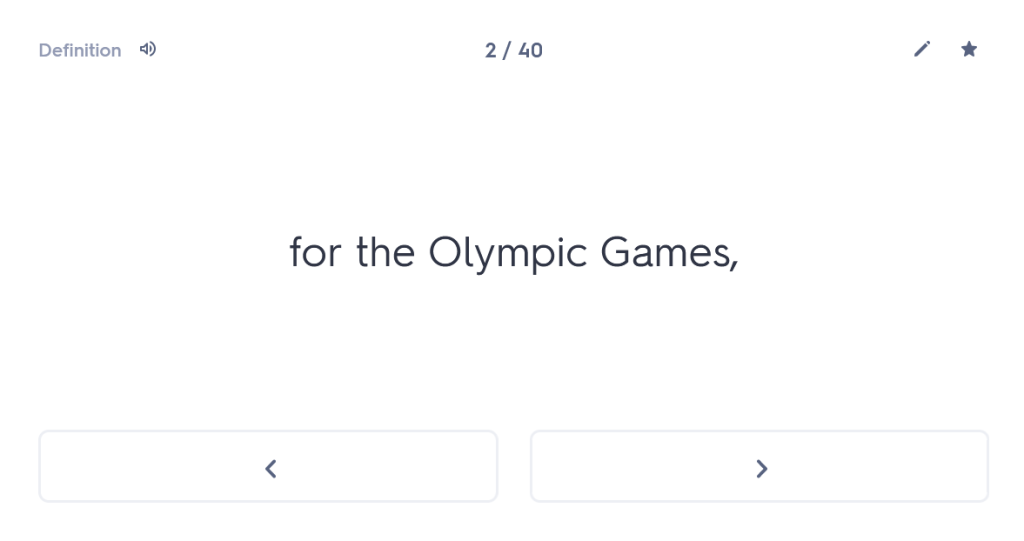
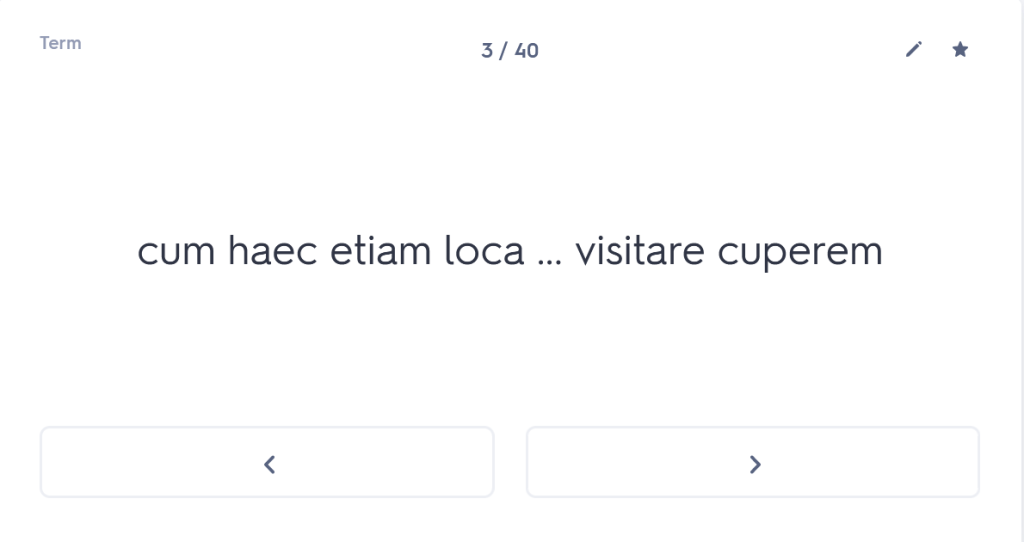
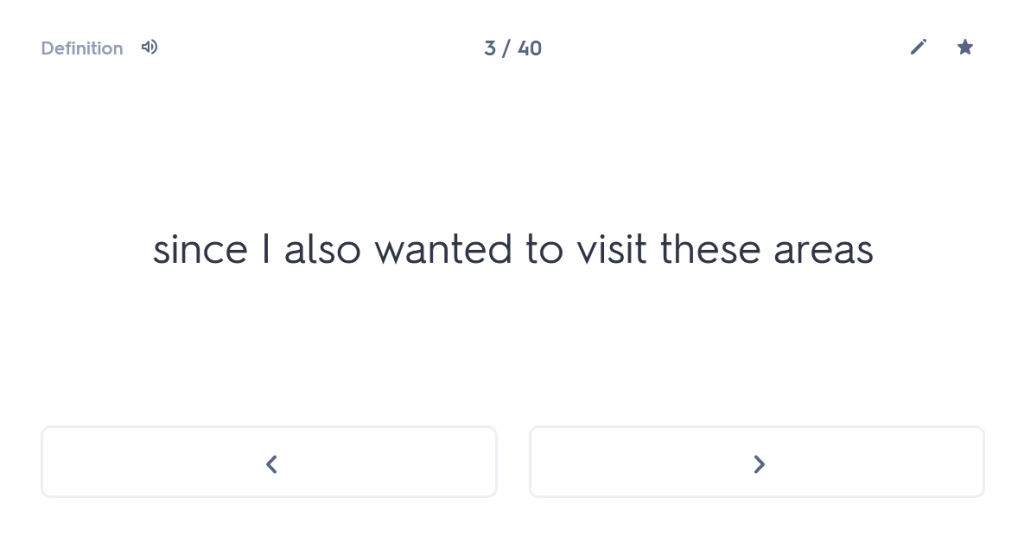
One of the best things about tutoring is the time and space to go back to basics. Many students come to me with a list of tricky constructions that they are struggling with, and without question I will address those things in the time I spend with them. More often than not, however, while the student may be requesting help with the ablative absolute or the indirect statement, what I discover is that they don’t even know their basic noun endings.
Over the years I have given a great deal of thought as to why this is so. The discovery – through tutoring – of just how many students this was true for certainly informed my own practice as a classroom teacher. I came to realise that the basics must revisited time and time again before students can claim full confidence and that this was true for all students, not just those that appeared to be struggling. So tutoring completely changed my approach in the classroom, for it gave the the realisation of just how much students naturally forget over time.
Given that Latin is a subject with which most people are unversed, I like to make analogies with subjects that are familiar to all of us. Imagine a child sitting their maths GCSE and trying to cope with the complexities of algebra and trigonometry. Then imagine that same child trying to sit their maths GCSE before they have fully grasped the meaning and process of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Maybe indeed you were that child. Maybe you were pushed through your GCSE or your O level with a shaky grasp of those basics. If you were that child, you will have been frankly terrified of maths as a subject and probably still believe that you’re “rubbish at maths”, all because nobody took the time to ensure that you understood the rudimentary basics. Remember how that felt? That’s what I’m talking about.
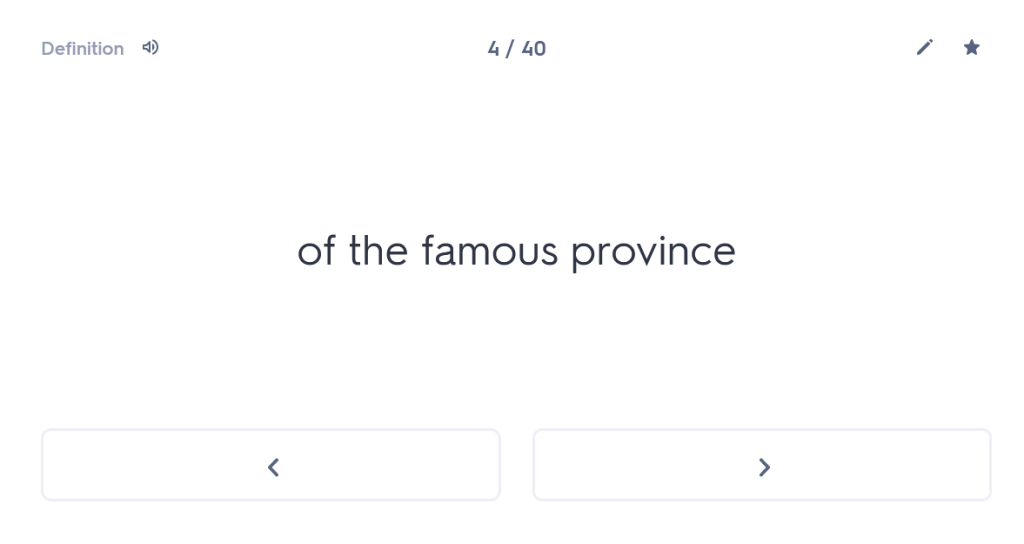
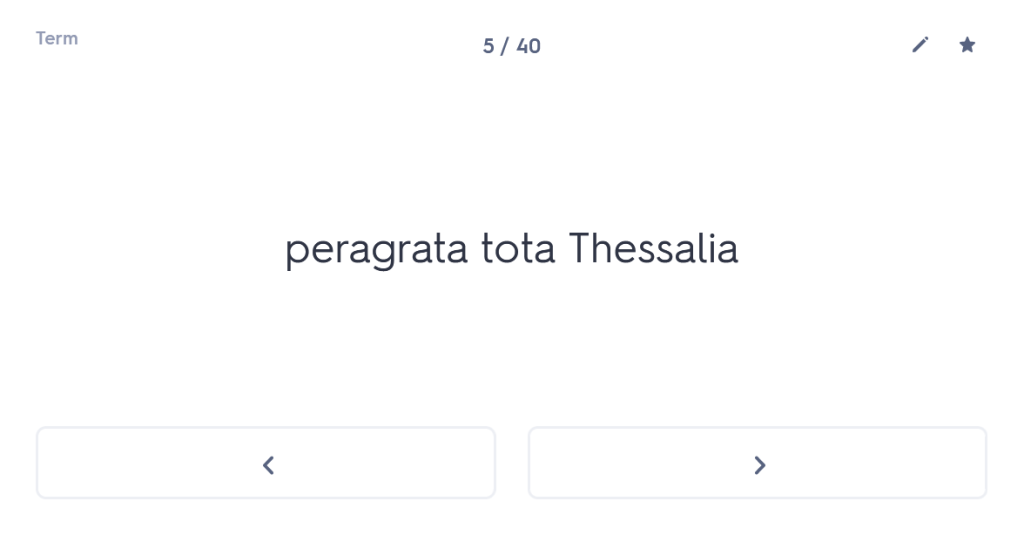
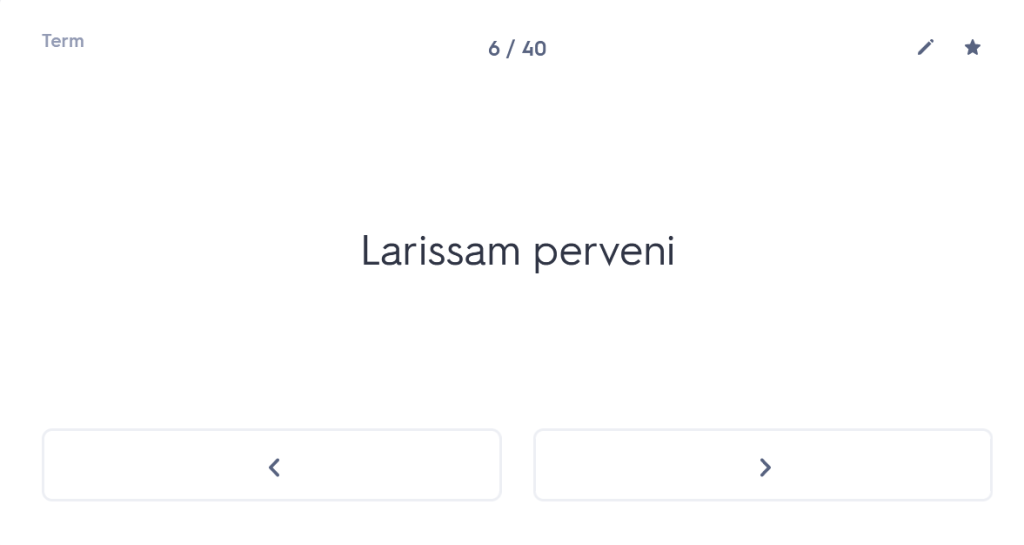
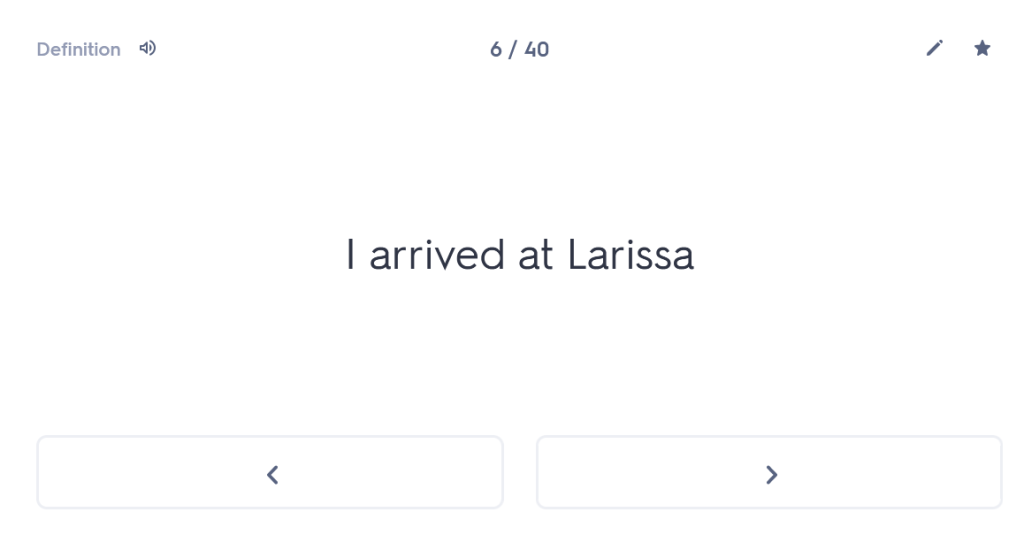
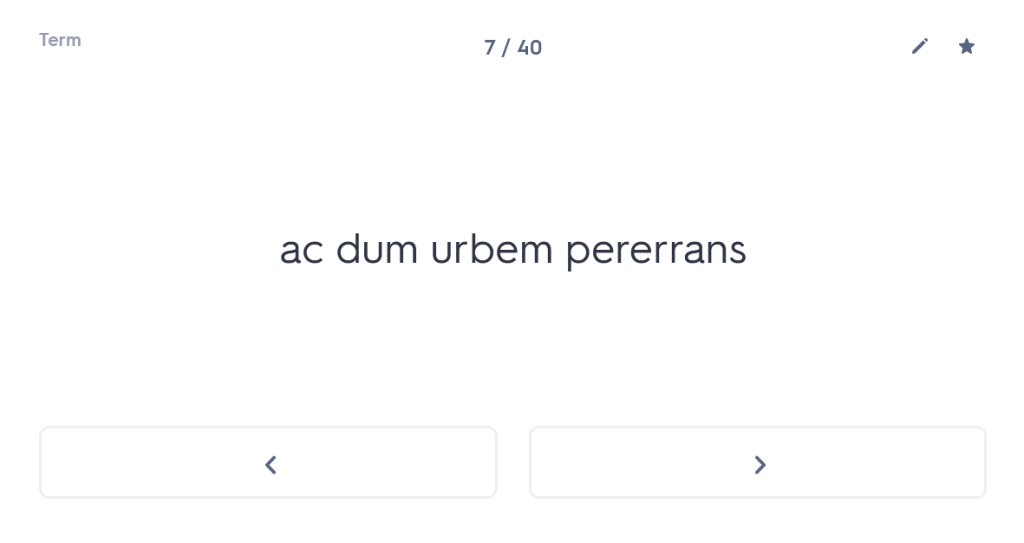
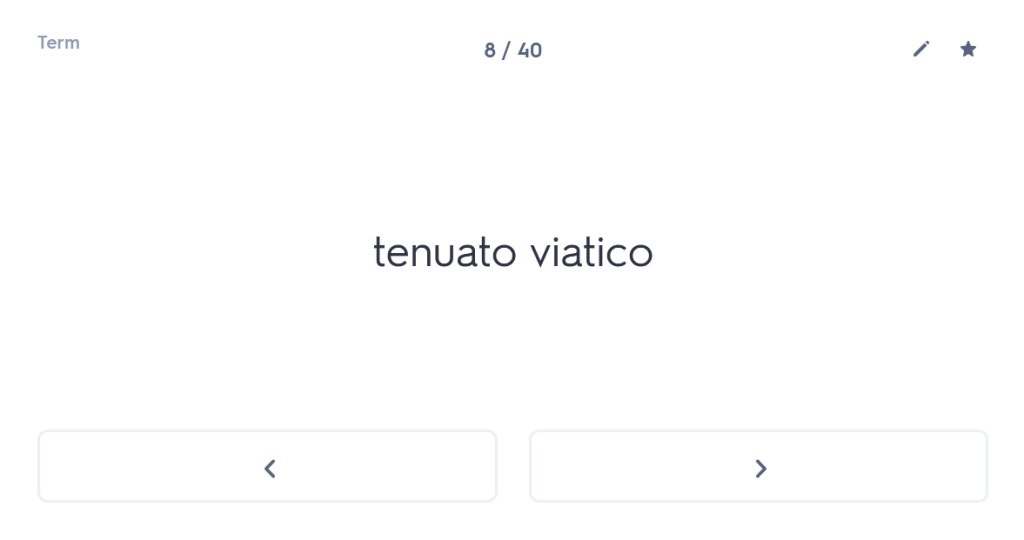
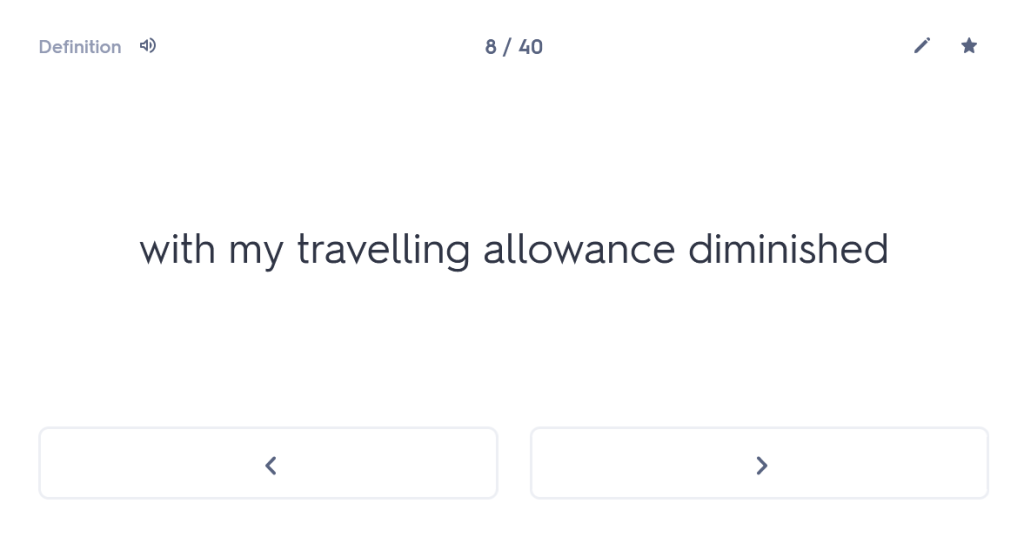
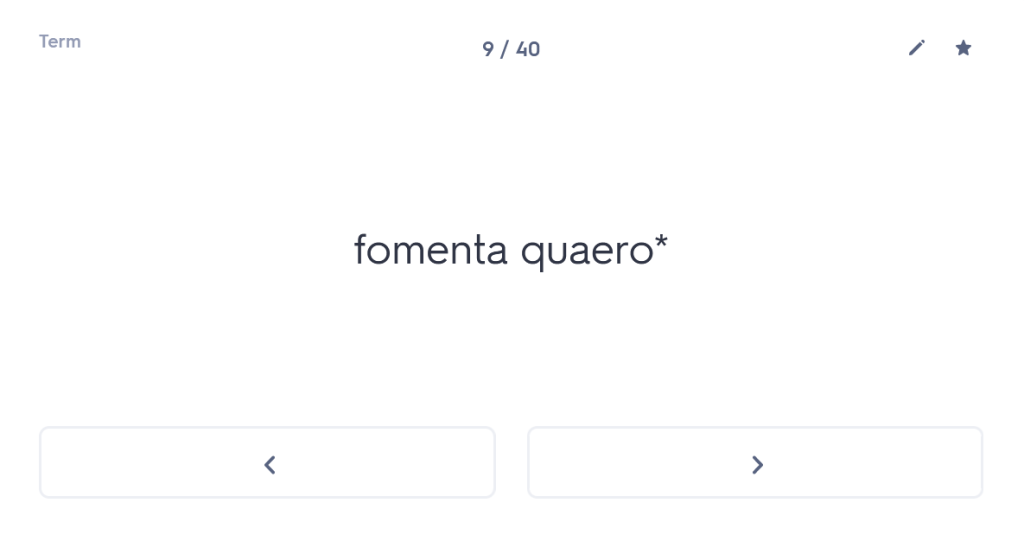
One of the first things I always check out when I meet a new student is whether they are confident with the order and meaning of the cases. You wouldn’t believe how many Year 10 or Year 11 students I have worked with who, when asked about this, have absolutely no idea. But what is the point of them learning their noun endings if they don’t know what those endings mean? So I start with a blank table and ask students whether they can tell me which case comes first and what the meaning of that case is. (Answer: nominative, and it’s the subject of the sentence). Most students who are taking GCSE are able to tell me this (although not all). Beyond that, many – not all, but the majority – start to fall apart from there. For example, they cannot remember whether the genitive comes before or after the dative and/or they cannot remember which one means “of” and which one means “to” or “for”. Immediately, therefore, we have a fundamental clue to what the underlying problem is with their approach to any Latin sentence: basically, in reality, they are guessing.
Delving into the gaps in a student’s knowledge like this is an enormous privilege and helping them start to plug those gaps is one of the best things about my job. All of these students have been taught these concepts before but all of them have forgotten that material. This is how memory works and this is why retrieval practice and revisiting past concepts in the classroom again and again is so crucial. Most classroom teachers, it seems to me, are still underestimating the importance of this and the extent to which even the highest of achievers need regular checks on their two times table interwoven with their introduction to the finer points of matrices. But the reality is that no matter how good the classroom teacher, no matter how solid and consistent their use of retrieval practice, there will still be some students who fall by the wayside; this may be due to illness causing absences or it may just be that they find it harder than the rest of the class. And that’s where tutoring comes in.
Sometimes people assume that repetition is boring and that working with lots of students on the same set of fundamentals would also be so. Nothing could be further from the truth. Every child is different and every child that is struggling in the classroom has their own personal and private worries; often a child has an instinct for the fact that they are missing some fundamental pieces of the puzzle but their situation has become so stressful that they feel unable to ask for help. Breaking down those barriers and helping them to grasp the core concepts and knowledge that they need in order to start succeeding is without a doubt the most rewarding thing that I could spend my time doing. Parents often tell me that their increased confidence and improving performance feels like a miracle.
So if your child is struggling with complex material, that is without doubt something which needs addressing. However, it may not be the case that the complex material is where we need to start. After many years of radio silence, I have recently taken up the piano again and am trying to re-learn some complex pieces that I could rattle off without hesitation at the age of 18. What I realised when I started at the music was that I have forgotten some of the most rudimentary bits of knowledge – when there are four sharps in the treble clef, what does that mean? I honestly can’t remember. So, before I can play with confidence, I will have to revisit some of those basics. I know that they will come flooding back, but the reality is that they need to be revised. So, back to basics I go. It will be worth it in the long-run.